It is a very promising choice to start a cassava starch business in Africa, because Africa is one of the main cassava producing areas, and cassava starch has a wide range of applications in food, industry and other fields. The following are the steps and strategies you can refer to:
I. Market research
1.1 Understand the current situation of the African cassava industry
Main production areas: Nigeria, Ghana, Tanzania, Mozambique, etc. are the main cassava producing areas in Africa.
Planting pattern: Understand the local cassava planting scale, variety, harvest season and output.
Supply chain status: Study the processing, transportation and sales channels of cassava starch.
1.2 Analyze market demand
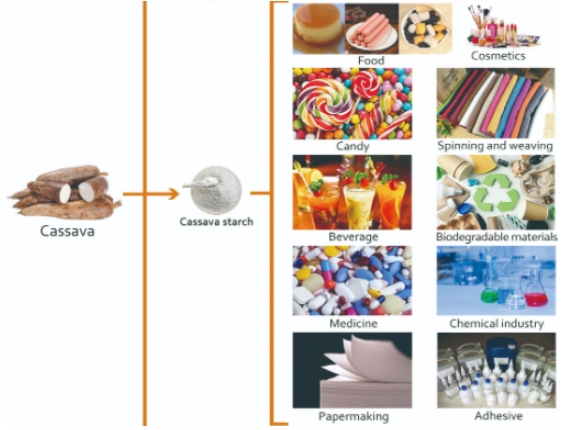
Food industry: Cassava starch is used for baking, condiments, snacks, etc.
Industrial field: Used for papermaking, textiles, glue, etc.
Feed industry: As a raw material for animal feed.
Export opportunities: Study the export demand and policies of African countries for cassava starch.
1.3 Competitor analysis
Understand the scale, products, prices and market share of local and international competitors.
Find out your competitive advantages, such as price, quality, service, etc.
II. Develop a business plan
2.1 Project positioning
Determine your target market (local sales, export or both).
Clarify product positioning (high-end, mid-end or low-end market).
2.2 Investment budget
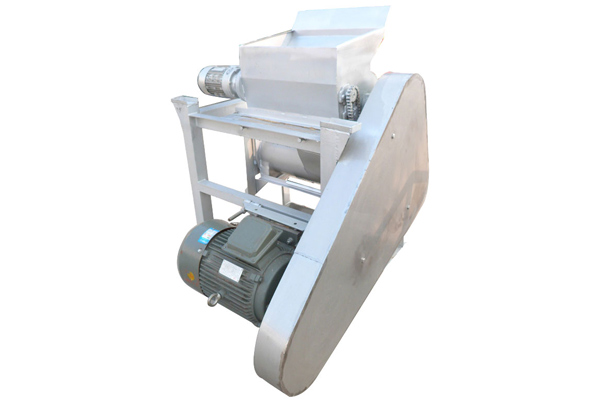
Equipment investment: cassava starch processing equipment (cleaning, crushing, dehydration, drying, packaging, etc.).
Plant construction: rental or construction costs of processing plants.
Operating funds: raw material procurement, labor costs, logistics costs, etc.
Working capital: used to cope with market fluctuations and emergencies.
2.3 Profit model
Make profits through the sale of cassava starch.
Explore the use of by-products (such as cassava residue) to increase income sources.
III. Site selection and plant construction
3.1 Site selection requirements
Close to the raw material production area: reduce the cost of raw material transportation.
Convenient transportation: facilitate product transportation and distribution.
Infrastructure: ensure stable water and electricity supply.
3.2 Plant construction
Design a plant layout that meets production needs.
Ensure that environmental protection meets standards and treat wastewater, waste residue, etc.
3.3 Equipment procurement
Select cassava starch processing equipment of appropriate scale.
Consider the degree of automation and energy efficiency of the equipment.
IV. Supply chain construction
4.1 Raw material procurement
Establish long-term cooperative relations with local farmers or cooperatives to ensure a stable supply of raw materials.
Set reasonable purchase prices to encourage farmers to grow cassava.
4.2 Production management
Establish strict production processes and quality control standards.
Train employees to improve production efficiency and product quality.
4.3 Logistics and warehousing
Establish an efficient logistics system to ensure that products are delivered to customers in a timely manner.
Build storage facilities to ensure the safe storage of raw materials and finished products.
V. Sales and marketing
5.1 Sales channels
Local market: sell through distributors, wholesalers, and retailers.
International market: expand export business through foreign trade companies or B2B platforms (such as Alibaba).
5.2 Pricing strategy
Set competitive prices based on costs and market conditions.
Provide bulk discounts or flexible payment methods for large customers.
5.3 Promotion strategy
Offline promotion: Participate in industry exhibitions and trade fairs to directly contact customers.
Online promotion: Promote products through social media, websites, and B2B platforms.
Word-of-mouth marketing: Win customer recommendations through high-quality products and services.
VI. Policy and compliance
6.1 Understand local policies
Study the investment policies, tax incentives and industry regulations of African countries.
Ensure that factory construction and operation comply with environmental protection, labor laws and other requirements.
6.2 Company registration
Register a company locally and obtain a business license and relevant permits.
Open a bank account to facilitate fund management.
6.3 Export procedures
Understand the tariffs, inspection and quarantine requirements for exporting cassava starch.
Apply for export licenses and related documents.
VII. Risk management
7.1 Market risk
Countermeasures: Diversify sales channels to avoid relying on a single market.
7.2 Raw material risk
Countermeasures: Cooperate with multiple suppliers to establish raw material reserves.
7.3 Exchange rate risk
Countermeasures: Use foreign exchange hedging tools to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
VIII. Partners and resource integration
8.1 Cooperate with local governments
Strive for policy support, such as tax incentives, subsidies, etc.
Participate in agricultural industrialization projects promoted by the government.
8.2 Cooperate with scientific research institutions
Introduce advanced technologies to improve production efficiency and product quality.
Develop high value-added products, such as modified starch.
8.3 Cooperate with international organizations
Cooperate with organizations such as the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) to obtain financial and technical support.
IX. Implementation plan
9.1 Short-term goals (within 1 year)
Complete market research and business plans.
Select a site to build a factory, purchase equipment, and start trial production.
9.2 Medium-term goals (2-3 years)
Expand production scale and increase market share.
Expand international markets and establish brand awareness.
9.3 Long-term goals (more than 5 years)
Become the leading cassava starch supplier in Africa.
Develop deep-processing cassava products and extend the industrial chain.

 EN
EN
 fr
fr  es
es  it
it  pt
pt